Key Takeaways:
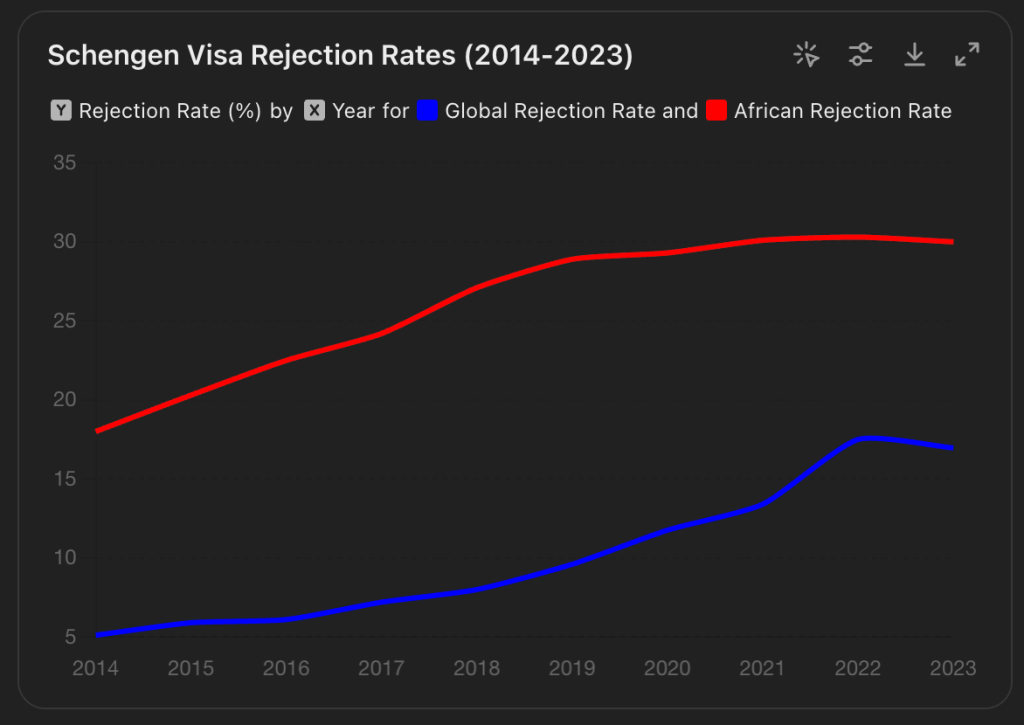
- Schengen visa rejections increased from 5% in 2014 to 17.5% in 2022 due to various geopolitical, economic, and social factors.
- Applicants face rejections due to strict migration policies, economic instability, incomplete documentation, and doubts about their intent to return.
- High rejection rates impact international relations, tourism, and impose significant economic burdens on applicants from specific nations.
Why Are Schengen Visa Rejections Increasing Each Year?
In recent years, Schengen visa rejections have seen a notable rise, significantly impacting applicants worldwide. From a global rejection rate of 5% in 2014 to a striking 17.5% in 2022, many wonder what factors are driving this increase, especially among applicants from African countries.

What Are the Reasons Behind Increasing Schengen Visa Rejections?
Multiple factors contribute to the rising Schengen visa rejections, involving geopolitical, economic, and social elements.
Geopolitical Factors
Migration Policies
Several European countries have tightened their migration policies in response to political instability and migration crises. This has led to more stringent scrutiny of visa applications, particularly from nations with high emigration rates.
Political Negotiations
Visa rejections can sometimes serve as leverage in political negotiations, especially with countries reluctant to accept deported nationals.
Economic Factors
Economic Instability
Applicants from economically unstable countries often face higher rejection rates. Authorities may doubt their ability to support themselves during their stay or their likelihood of returning home.
Financial Requirements
Many applicants fail to meet the financial requirements, such as proving sufficient funds for their stay. This remains a common reason for visa denials.
Social Factors
Documentation Issues
Incomplete or falsified documentation is a primary cause of visa rejections. Applicants must provide complete and accurate documents, including proof of accommodation, travel insurance, and a clear travel itinerary.
Intent to Return
Applications often get rejected if authorities doubt the applicant’s intention to return to their home country. Strong ties to the home country, like stable employment or family responsibilities, are crucial for a successful application.
How Have International Events Affected Schengen Visa Applications?
International events like the COVID-19 pandemic and ongoing migration crises have further complicated the visa application process.
COVID-19 Pandemic
The pandemic had a profound impact on visa policies and application processes. Travel restrictions and health concerns initially led to a drop in applications. However, as countries remained cautious during the recovery period, rejection rates surged.
Migration Crises
Europe faces continued migration crises, particularly from Africa and the Middle East. This influx has made countries more stringent in their visa issuance policies to manage asylum seekers and unauthorized migrants better.
Profiles of Commonly Rejected Applicants
Nationalities Facing the Highest Rejection Rates
Applicants from Algeria, Guinea-Bissau, Nigeria, Ghana, Senegal, and Mali often face rejection rates exceeding 40%. Those from countries with high asylum rates like Syria and Pakistan also experience significant visa rejections.
Purpose of Visit
Tourist and business visas are more likely to be rejected compared to student or family reunion visas. Authorities often suspect tourists and business visitors might overstay their visas.
Demographic Characteristics
Younger applicants and individuals without strong economic ties to their home countries face higher rejection rates.
Which Schengen States Have the Highest and Lowest Rejection Rates?
Highest Rejection Rates
- Malta: 37.6%
- Sweden: 29%
- Belgium: 28.4%
- France: 22.2%
Lowest Rejection Rates
- Iceland: 2.2%
- Switzerland: 10.7%
- Latvia: 11.7%
What Are the Consequences of Rising Schengen Visa Rejection Rates?
Impact on International Relations
High rejection rates can strain diplomatic relations, especially with countries that perceive these policies as discriminatory or politically motivated.
Tourism and Global Mobility
Increased rejection rates deter tourists and business travelers, negatively impacting the tourism industry and economic exchanges between countries.
Economic Impact on Applicants
Rejected applicants incur significant costs, including non-refundable visa fees, travel expenses, and lost opportunities for business or education.
How Have Geopolitical Events Influenced Schengen Visa Rejection Rates Over The Past Decade?
Overview of Trends
Schengen visa rejection rates have significantly increased over the past decade, rising from 5% in 2014 to 17.9% in 2022, and slightly decreasing to 16% in 2023. This trend is particularly severe among applicants from African and Asian countries.
Migration Crises
Migration crises, especially from Syria, Iraq, Afghanistan, and other conflict zones, have profoundly impacted Schengen visa policies. By the end of 2016, nearly 5.2 million refugees and migrants had reached Europe, prompting stricter visa scrutiny.
Political Instability
Political instability in various regions contributes to higher rejection rates. Countries experiencing significant turmoil, such as Syria, Pakistan, and many African nations, see higher rejection rates due to concerns about applicants’ intentions to overstay or seek asylum.
For instance, Syrian nationals faced a rejection rate of 45.9% in 2023, reflecting ongoing conflicts and high asylum application rates from this group.
Economic Sanctions and Diplomatic Relations
Strained diplomatic relations also play a significant role. Turkish nationals have faced increasing rejection rates, attributed partly to political decisions amidst strained EU-Turkey relations. Similarly, visa rejections for Russian applicants have been influenced by geopolitical tensions following the annexation of Crimea and the ongoing conflict in Ukraine.
COVID-19 Pandemic
The pandemic disrupted global mobility, causing temporary border closures and stricter entry requirements. Although initially lowering visa applications, a more cautious approach to visa issuance during the recovery period increased rejection rates.
Which Countries Face the Highest Rejection Rates?
High-Rejection Countries
Countries with high rejection rates often share these characteristics:
- Low GDP per capita
- High emigration and asylum application rates
For instance, nationals from Comoros, Guinea-Bissau, Ghana, Mali, Guinea, and Senegal faced rejection rates between 41% and 57% in 2023.
Specific Rejection Rates
- Malta: 36.4%
- Sweden: 29%
- Belgium: 28.4%
- France: 22.2%
- Iceland: 2.2%
- Switzerland: 10.7%
- Latvia: 11.7%
What Are the Broader Implications of Rising Visa Rejections?
International Relations
High rejection rates can strain diplomatic ties with countries perceiving these policies as discriminatory.
Tourism and Global Mobility
Increased rejection rates deter travelers, impacting tourism and economic exchanges.
Economic Impact on Applicants
Affected applicants bear significant costs, including non-refundable fees and missed educational or business opportunities.
Conclusion
The rising rejection rates for Schengen visas result from a complex interplay of geopolitical, economic, and social factors. Addressing these challenges requires a balanced approach, considering both security concerns and the need for fair and transparent processes. Understanding the underlying reasons and trends is crucial for applicants and policymakers alike.
For more information, visit the official European Commission Visa Information here.
According to VisaVerge.com, efforts to understand and mitigate visa rejections can improve international relations and economic exchanges between nations.
Learn Today:
Glossary
- Schengen Visa: A visa that allows travel to any of the 26 European countries that make up the Schengen Area, enabling free movement and short stays of up to 90 days within a 180-day period.
- Migration Policies: Governmental regulations and laws designed to control and manage the movement of people across national borders, including those concerning immigration, asylum, and deportation.
- Financial Requirements: Criteria set by visa-issuing authorities requiring applicants to demonstrate that they have sufficient financial resources to support themselves during their stay in the Schengen Area.
- Intent to Return: Evidence that visa applicants must provide to show that they plan to leave the Schengen Area after their permitted stay, often demonstrated through ties to their home country such as employment or family responsibilities.
- Geopolitical Factors: Political conditions and relationships between countries that impact visa issuance policies, including international negotiations, political instability, and migration crises.
This Article In A Nutshell:
Schengen visa rejections have surged, increasing from 5% in 2014 to 17.5% in 2022. Reasons include stricter migration policies, economic instability, and incomplete documentation. African and Middle Eastern applicants face the highest rejection rates. This trend affects global tourism, international relations, and individual economic opportunities.
— By VisaVerge.com
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for informational purposes only. If you reference or use any content from this article, please attribute it to VisaVerge.com by including a link to the original source. We appreciate your adherence to our content usage policies and your commitment to giving proper credit.














