Key Takeaways:
- The Final Rule to Update Immigration Fees will increase H-1B visa fees by 70% and H-1B cap lottery fees to $215.
- Permanent residency and citizenship fees will also increase, affecting naturalization and EB-5 Investor Visa Program applicants.
- The fee increases could deter businesses from sponsoring foreign talent, potentially disrupting the U.S. job market.
Immigration Visa Fee Increase: H-1B and Permanent Residency Costs on the Rise
The landscape of U.S. immigration is about to change with the latest update from USCIS. The Final Rule to Update Immigration Fees, under the code 1615-AC68, has just cleared White House review—marking a significant shift in the financial aspect of U.S. immigration processes. Here, we delve into the specifics of this pivotal development.
H-1B Visa Fees Increase: The Impact on Applicants and Employers

One of the most notable aspects of this new rule is the substantial increase in H-1B Visa application fees. Typically sought by professionals in specialty occupations, the fee for this visa is set to climb by a staggering 70% from the current $460 to an anticipated $780.
But the fee hikes don’t end there. Registrants of the H-1B cap lottery, who are currently paying $10 for E-registration, will soon see this fee skyrocket to $215. This marks a significant change that could affect countless potential applicants and the sectors that depend on their skills.
“The proposed H-1B Visa fees increase will have a profound effect on individuals and companies. This significant rise might deter businesses from sponsoring foreign talent, which in turn could reshape the U.S employment landscape.”
The upcoming H-1B cap season in March 2024 won’t see these changes come into effect immediately, but businesses and applicants should be aware of the likely fee adjustments in the future.
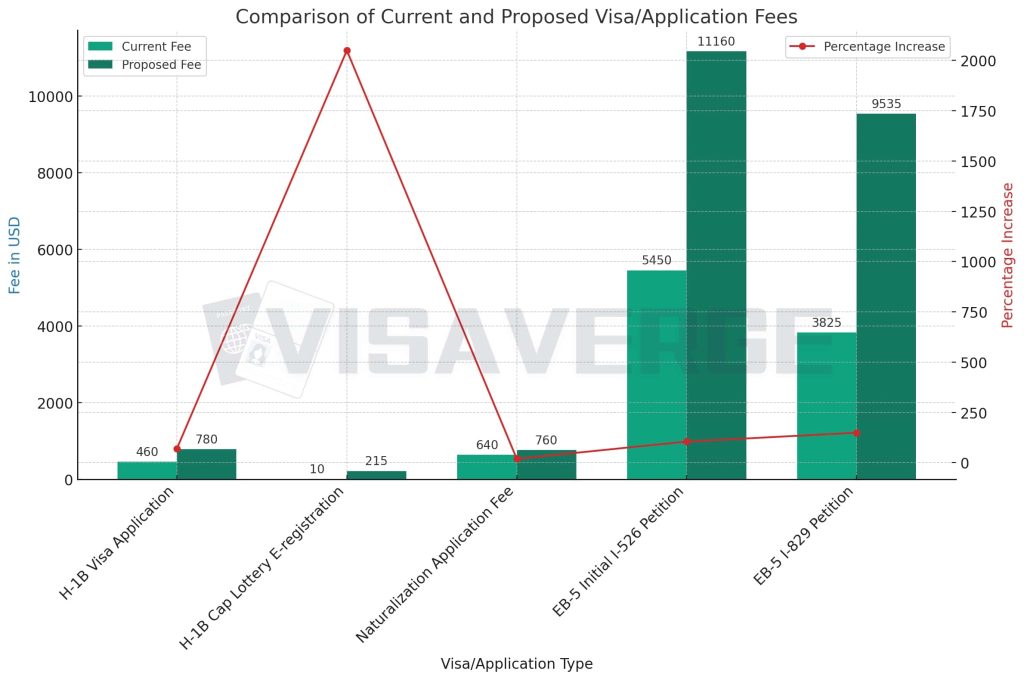
- The blue bars represent the current fees for each visa/application type.
- The orange bars show the proposed fees.
- The red line with markers indicates the percentage increase for each category.
Permanent Residency and Citizenship Fees Also Set to Increase
The ripples from the Clears White House Review extend to those seeking permanent residency or U.S citizenship. The shift in fees is not isolated to temporary work visas alone. Proposed changes include:
- A 19% increase in the naturalization application fee, from $640 to $760.
- A significant update to the EB-5 Investor Visa Program where initial I-526 petition fees could potentially double from the current $5,450 to $11,160.
- The I-829 petition fees, crucial for removing conditions on residency, could see nearly a 150% jump from $3,825 to $9,535.
These figures highlight not only the financial commitment required by prospective immigrants but also point to the economic implications for U.S. employers.
| Visa/Application Type | Current Fee | Proposed Fee | Percentage Increase | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H-1B Visa Application | $460 | $780 | 70% | Fee paid by employers for each H-1B visa petition. |
| H-1B Cap Lottery E-registration | $10 | $215 | 2050% | Fee paid for entering the H-1B cap lottery process. |
| Naturalization Application Fee | $640 | $760 | 19% | Fee paid by individuals applying for U.S. citizenship. |
| EB-5 Initial I-526 Petition | $5,450 | $11,160 | 105% | Fee paid by investors applying for the EB-5 Investor Visa. |
| EB-5 I-829 Petition | $3,825 | $9,535 | 149% | Fee for removing conditions on residency for EB-5 Visa. |
Economic Implications for U.S. Businesses
With the proposed fee increases, companies must remain vigilant. The additional costs of sponsoring foreign workers through H-1B Visas could cause hesitation in the recruitment process, potentially disrupting the inflow of specialized skill sets into the U.S. market.
Furthermore, the recent hike in premium processing fees, which have gone up by 12% to a total of $2,805, poses additional financial planning challenges for employers. It is crucial for businesses to incorporate these changes into their financial projections and hiring strategies.
Responding to the Change
The fee adjustment proposal is not set in stone yet, it’s already making waves. Businesses, along with individuals aiming to live and work in the U.S, should stay informed on the progression of these changes.
For more detailed and authoritative information, prospective visa applicants and U.S. employers are encouraged to visit the official USCIS website or consult with immigration professionals.
It’s important to keep an eye on updates as the USCIS is funded almost entirely by user payments and these fees, not updated since 2016, are crucial for its operation and services. The proposed increases underscore the agency’s need to maintain its financial viability while delivering essential immigration services.
As these proposed fee adjustments prepare to take effect, the U.S. immigration system braces for widespread impact spanning individuals’ ambitions to America’s economic fabric. Stakeholders should prepare, adapt, and strategically plan for these imminent changes.
Learn Today:
Glossary or Definitions:
- USCIS: The United States Citizenship and Immigration Services is a government agency responsible for processing immigration-related applications, petitions, and requests, including those for visas and permanent residency.
H-1B Visa: A non-immigrant visa category for foreign workers in specialty occupations that require specialized knowledge. This visa allows U.S. employers to temporarily hire foreign workers in occupations such as technology, engineering, science, and finance.
Specialty Occupation: A job that requires theoretical and practical application of a highly specialized body of knowledge and a bachelor’s degree or higher in a specific field or its equivalent.
Visa Fees: The monetary charges imposed by the government for the processing and adjudication of visa applications, petitions, or other immigration-related requests.
Final Rule: A regulatory action published by a federal agency to establish new regulations or modify existing regulations in accordance with the Administrative Procedure Act. In this context, the Final Rule refers to the rule issued by USCIS to update immigration fees.
Cap Lottery: The process where a limited number of H-1B visas are made available each fiscal year, and if the number of applications exceeds the annual cap, USCIS conducts a lottery to randomly select the petitions that will be eligible for processing.
Permanent Residency: Also known as a green card, it is an immigration status that allows foreign nationals to live and work permanently in the United States.
U.S. Citizenship: The status of being a citizen of the United States, acquired either by birth or through the naturalization process.
Naturalization Application: The process by which a foreign national becomes a U.S. citizen by meeting certain eligibility requirements, including residency, language proficiency, and good moral character, and by taking an oath of allegiance.
EB-5 Investor Visa Program: A program that provides an opportunity for foreign investors to obtain permanent residency in the United States by making a significant investment in a new commercial enterprise that creates jobs for U.S. workers.
I-526 Petition: The initial petition filed by an EB-5 investor to establish their eligibility for the EB-5 program, providing evidence of their capital investment and the job creation potential.
I-829 Petition: The petition filed by an EB-5 investor to remove the conditions on their permanent residency status, demonstrating that the required investment has been sustained and job creation has occurred.
Premium Processing Fees: Optional fees that can be paid to expedite the processing of certain immigration-related applications or petitions, typically resulting in a faster adjudication.
Financial Projections: Forecasts or estimates of future financial performance based on assumptions and analysis of past and current financial data.
Immigration Professionals: Individuals or organizations that are knowledgeable and experienced in immigration law and procedures, providing services and advice to individuals and employers regarding immigration matters.
Financial Viability: The ability of an organization or agency to sustain its financial operations and meet its financial obligations.
Stakeholders: Individuals or groups who have an interest or concern in a particular issue or industry, in this context, referring to individuals, employers, and organizations affected by immigration policies and regulations.
The recent proposal to increase immigration fees has far-reaching implications for applicants, companies, and the U.S. economy. The rising costs of H-1B visas and permanent residency applications could deter businesses from sponsoring foreign talent and disrupt the inflow of specialized skills. To stay informed and prepared, visit visaverge.com for authoritative information and expert guidance on navigating these changes. Don’t miss out on the latest updates and opportunities in U.S. immigration!
This Article in a Nutshell:
The recent update from USCIS on the Final Rule to Update Immigration Fees will impact the costs of H-1B visas and permanent residency applications. H-1B visa fees will increase by 70%, potentially deterring businesses from sponsoring foreign talent. Permanent residency and citizenship fees will also rise. This has economic implications for US employers and prospective immigrants. USD2825














