Key Takeaways
• On January 20, 2025, President Trump signed the “Protecting the American People Against Invasion” (PAPAI) order, targeting sanctuary jurisdictions via punitive measures.
• PAPAI expands § 287(g) agreements, allowing local law enforcement to perform immigration tasks; Homeland Security Task Forces are established nationwide.
• PAPAI mandates increased detention capacity and expedited removal processes; civil rights groups warn of racial profiling and due process violations.
President Trump’s latest executive actions signal a significant escalation in immigration enforcement throughout the United States. As of February 20, 2025, states are reacting differently to these new federal efforts aimed at deporting undocumented immigrants. With some states actively cooperating and others moving to protect their immigrant populations, the debates surrounding Trump’s deportation plans are intensifying.
On January 20, 2025, President Trump signed the executive order titled “Protecting the American People Against Invasion” (PAPAI). This order lays out a strategy for stricter immigration enforcement, including immediate action against sanctuary jurisdictions—cities or states that limit cooperation with federal immigration agencies. PAPAI directs punitive measures against these jurisdictions, such as withholding federal funding, and urges the Attorney General and the Secretary of Homeland Security (DHS) to ensure compliance. This approach directly challenges sanctuary policies, which many local governments argue are necessary to protect immigrant communities and maintain public trust.
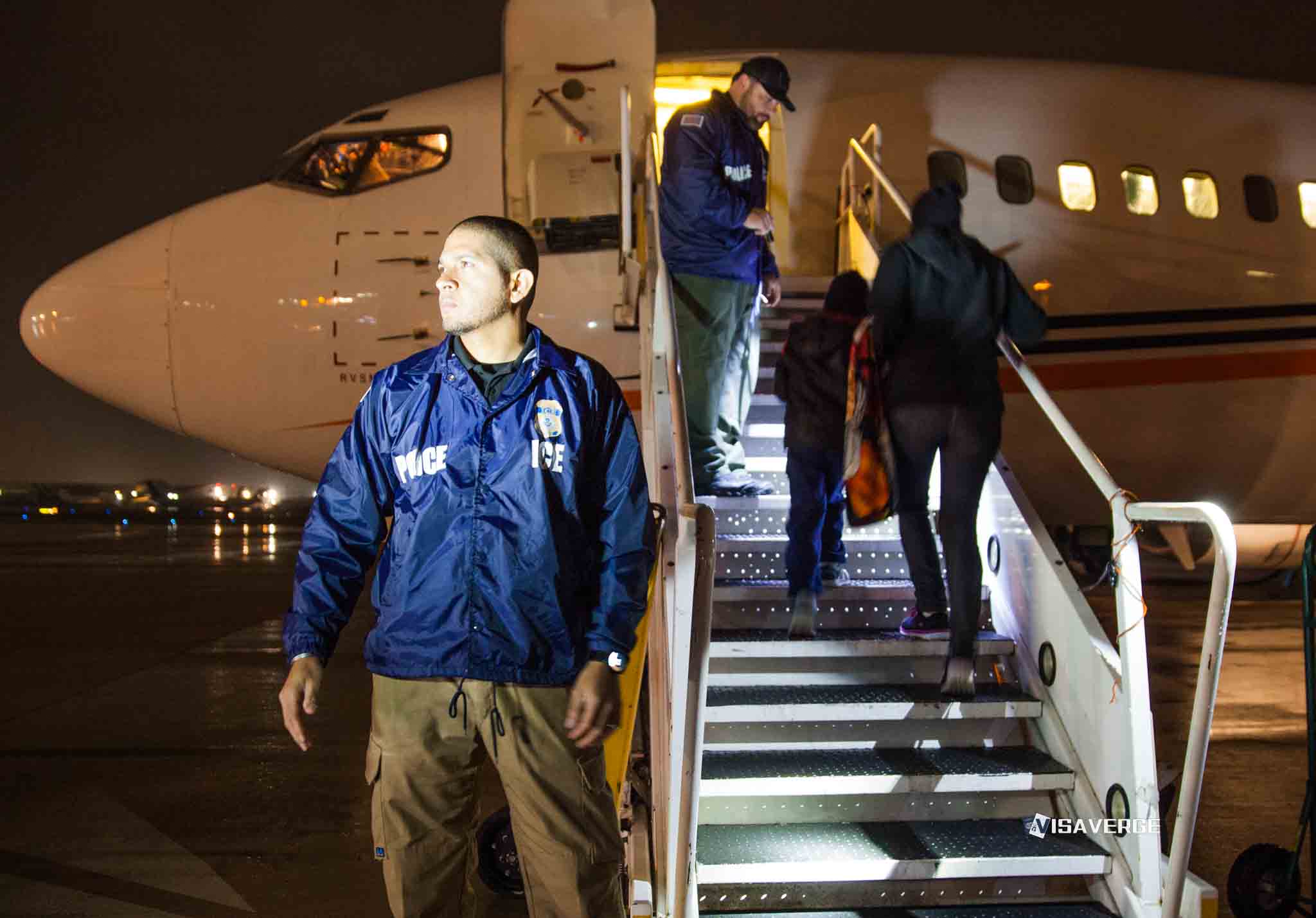
A core component of PAPAI is the expansion of agreements under § 287(g) of the Immigration and Nationality Act (INA). This program allows DHS to train local law enforcement officials to perform immigration-related tasks, such as identifying, detaining, and handing over undocumented individuals for deportation. The Trump administration has called for these agreements to be extended “to the maximum extent permitted by law.” If widely adopted, § 287(g) agreements would significantly increase the capacity for immigration enforcement by involving local police in federal operations.
To coordinate efforts, Homeland Security Task Forces are being set up across all 50 states. These task forces aim to root out criminal cartels, foreign gangs, and human trafficking networks, while ensuring the robust enforcement of existing immigration laws. Their sweeping mandate, however, has raised concerns about potential overreach, including racial profiling and strained relationships between immigrant communities and law enforcement.
Some states, such as Texas, appear eager to work alongside federal agencies on these initiatives. Texas had previously attempted its own state-level deportation efforts with SB 4, a controversial law that was blocked by courts for overstepping constitutional limits. With renewed federal backing, Texas and states with similarly conservative policies may push for active roles in immigration enforcement. This could include ramping up their cooperation with federal programs like § 287(g).
On the other hand, resistance is growing in states and cities that have adopted sanctuary policies. These jurisdictions, which include California 🇺🇸 and New York City 🇺🇸 among others, have vowed to limit their assistance with Trump’s deportation plans. Many argue that cooperating with federal authorities could erode trust between immigrant communities and the police, making it harder to address local crime effectively. PAPAI poses a direct challenge to these sanctuary jurisdictions by requiring compliance with 8 U.S.C. § 1373, a federal law prohibiting restrictions on sharing immigration status information.
Sanctuary jurisdictions have a long history of legal battles with federal authorities, dating back to President Trump’s first term. In January 2017, Trump issued an executive order targeting these regions, prompting lawsuits and temporary court blocks. While the 2017 order set the stage for today’s policies, the aggressive nature of PAPAI has sparked fears of unprecedented enforcement measures.
To counter these challenges, some states are taking proactive steps to safeguard their immigrant populations. A number of local governments have allocated funds for legal representation for undocumented families and individuals facing deportation. Others are forming networks to monitor enforcement activities, ensure transparency, and address issues like unauthorized stops or racial discrimination. These measures aim to support immigrants as they confront increasingly complex legal hurdles.
That said, President Trump’s deportation plans face substantial obstacles beyond political resistance. The current immigration system lacks the capacity to process the large-scale deportations proposed under PAPAI. To tackle this, the administration is exploring options to expedite removal procedures, such as applying “expedited removal” to a broader group. Expedited removal allows immigration officers to deport individuals without a court hearing if they don’t have proper legal documents and meet other criteria. Critics warn these measures could undermine due process rights, prompting inevitable legal challenges.
The Trump administration is also considering invoking the Alien Enemies Act, a law rarely used in modern times, to justify strict immigrant detentions. This has raised additional constitutional concerns, as courts have long confirmed that only the federal government—not states or localities—can wield such authority. For example, the legal blockade of Texas’s SB 4 underscores the judiciary’s role in limiting overreach.
Another focal point of PAPAI is the expansion of detention capacity. The order directs DHS to allocate resources for constructing new detention facilities to eliminate so-called “catch-and-release” practices. These facilities aim to detain more individuals awaiting removal, although this effort will require significant congressional funding—a challenge given the split opinions in Washington.
Beyond enforcement, PAPAI outlines financial disincentives for immigration violations. It mandates DHS to assess fines against individuals who entered or remained in the country without lawful status, as well as those who help them. By imposing these penalties, the administration hopes to encourage compliance with immigration laws. Additionally, voluntary departure programs, where individuals return to their home countries on their own instead of being formally deported, are being expanded as part of these efforts.
In a surprising move, Acting DHS Secretary Benjamine Huffman issued an order granting immigration enforcement authority to officers from non-specialized federal agencies. This includes the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) and the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, and Firearms (ATF), among others. While intended to strengthen enforcement capabilities, this decision has raised questions about whether agencies with limited immigration experience can fulfill these duties without infringing on civil rights.
The administration wasted no time putting its policies into action. On President Trump’s first full day back in office, federal officers conducted enforcement operations in multiple sanctuary cities. Reports suggest that more than 300 arrests were made in these areas, targeting individuals classified as “illegal migrant criminals.” Border Patrol officials also observed a 35% drop in southern border crossings during Trump’s initial days compared to the final days under President Biden.
While the administration celebrates these early efforts, the long-term impacts remain uncertain. For immigrant communities, the heightened role of local police in federal enforcement could lead to fear and distrust, discouraging individuals from reporting crimes or seeking help. Civil rights advocates warn of potential racial profiling and unlawful detentions under expanded § 287(g) programs and Homeland Security Task Forces.
Some experts highlight the economic effects of mass deportations on Latin American nations, where many of these individuals may be sent. A sudden influx of deportees could overwhelm fragile economies, exacerbate unemployment, and destabilize regions already struggling with limited resources.
Looking ahead, it’s clear that the Trump administration’s immigration policies will continue to spark legal battles, political debates, and passionate discussions in communities across the country. While states like Texas are embracing PAPAI’s aggressive provisions, others are forging plans to protect immigrants and challenge federal mandates in court.
As analysis from VisaVerge.com suggests, the intersection of state and federal authority remains a contentious issue, one that will likely define the coming months. For individuals and families directly impacted, understanding changing legal frameworks and accessing legal resources will be crucial. To explore official details on § 287(g) agreements and how they operate, readers can visit the U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement webpage for accurate information.
In conclusion, the landscape of immigration enforcement in the United States is shifting rapidly under the Trump administration. Balancing enforcement goals with constitutional protections and the priorities of state and local governments presents a formidable challenge, with far-reaching implications for immigrant communities and the nation as a whole.
Learn Today
PAPAI (Protecting the American People Against Invasion) → An executive order enforcing stricter immigration measures, targeting sanctuary jurisdictions and expanding deportation efforts in the U.S.
Sanctuary Jurisdictions → Cities or states limiting cooperation with federal immigration agencies to protect immigrant communities and maintain public trust.
§ 287(g) Agreements → Program allowing local law enforcement to perform immigration-related duties under training and supervision by federal authorities.
Expedited Removal → Process enabling immigration officers to deport individuals without court hearings if they lack legal documentation and meet specific criteria.
Alien Enemies Act → A rarely invoked law permitting stringent detention measures against individuals from nations considered hostile during conflicts.
This Article in a Nutshell
President Trump’s 2025 immigration order, PAPAI, ignites nationwide debate. While Texas embraces strict federal enforcement, sanctuary states like California resist, citing community trust. Key policies include expanded local-federal collaboration and rapid deportation processes, sparking legal challenges over civil rights and due process. Immigration policy now balances enforcement, constitutional protections, and state autonomy—shaping America’s future.
— By VisaVerge.com
Read more:
• Birthright Citizenship in the United States: Myths vs. Facts
• ICE Detainees Moved to Border States in First Large Transfer Under New Policy
• Federal Judge Blocks Donald Trump’s Spending Freeze as 22 States Sue
• States Sue Over Trump’s Birthright Citizenship Ban
• CBP Reinstates ‘Alien’ Term for Noncitizens and Migrants








