Key Takeaways
- Trump’s proposed mass deportation could severely disrupt industries reliant on immigrant labor, causing labor shortages and economic upheaval.
- Key sectors like agriculture, construction, hospitality, and retail would face workforce crises leading to increased prices and production challenges.
- Large-scale deportations risk economic impacts including GDP decline, reduced tax revenues, and widespread social and familial disruptions.
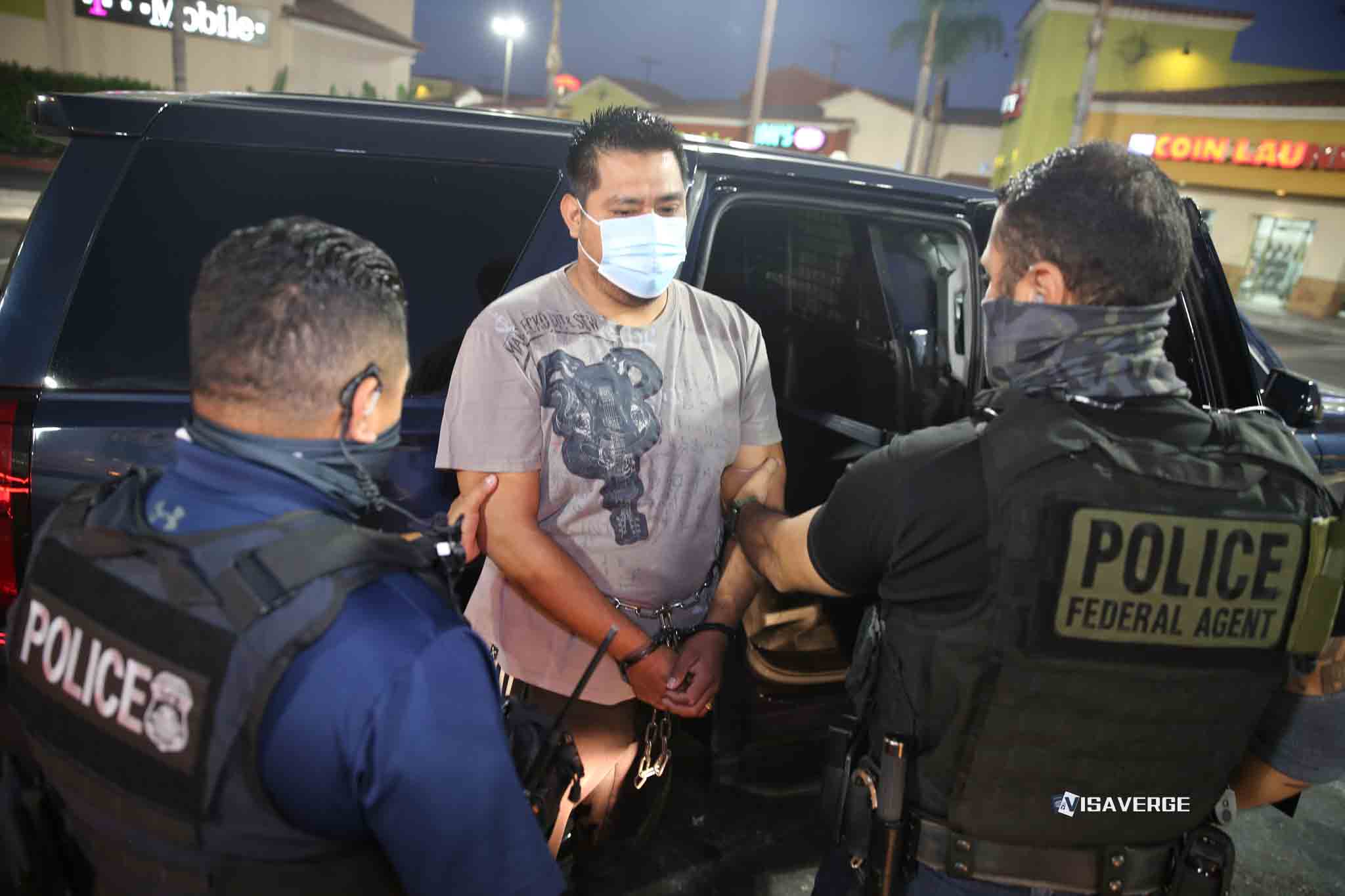
The potential mass deportation policy proposed by Donald Trump, aimed at removing millions of undocumented immigrants from the United States, is a topic stirring widespread concern among many key stakeholders, including economists, industry leaders, and policymakers. This proposal could deeply impact several industries that are heavily reliant on immigrant labor, including agriculture, construction, hospitality, and retail. In this comprehensive analysis, we explore the far-reaching implications of such a policy, discussing expected labor shortages, price increases, and economic disruptions that might follow.
Agriculture: The Backbone at Risk
Among the most vulnerable industries is agriculture. Immigrant labor, particularly undocumented workers, forms a substantial portion of the workforce in this sector. Estimates suggest that more than half of all farm workers in the U.S. are undocumented immigrants. Without this key labor supply, farms would face significant challenges in maintaining current production levels, which could cause major disruptions across the food supply chain.
If these workers were deported, we could witness food shortages and a sharp rise in prices for essential goods like fruits and vegetables. To illustrate, immigrant labor is integral to dairy farms, which produce nearly 80% of the U.S. milk supply. A sudden reduction in this workforce could potentially double milk prices. Seasonal crops requiring intensive labor could face dire shortages, as there is no ready pool of domestic workers eager to step into these labor-intensive roles.
Construction: An Industry Already Under Strain
The construction industry faces similar issues given its heavy reliance on immigrant labor. In states like Texas 🇺🇸 and California 🇺🇸, immigrants—documented and undocumented—constitute up to 40% of the construction workforce. Removing these workers could exacerbate an already critical labor shortage, hindering the industry’s ability to meet demand, especially in areas recovering from hurricanes or experiencing housing shortages.
Already grappling with a workforce shortfall of about 400,000 workers, the industry would struggle to assemble the crews needed for large-scale projects such as new home construction or infrastructure development. Failing to meet this demand could result in fewer homes being built, ultimately driving up housing costs. Infrastructure projects might also face significant delays or be canceled outright due to a lack of available labor.
Hospitality and Retail: Facing Severe Disruptions
The hospitality and retail sectors would also confront considerable disruptions under such a mass deportation policy. Immigrants represent around 8% of the workforce in these industries, frequently filling lower-wage positions that domestic workers are less likely to take. During the COVID-19 pandemic, the hospitality sector already faced service disruptions and price increases due to worker shortages. A prolonged and intensified shortage, spurred by significant deportations, could cripple these industries, pushing some businesses to reduce hours or close, while others might see service quality decline due to staffing shortages.
Broader Economic Consequences
Labor Market Turmoil
A dramatic workforce reduction would likely ensue if mass deportation policies were enacted. Around 5% of the U.S. labor force consists of undocumented immigrants, but this percentage can spike significantly in specific industries like agriculture and construction. The removal of these workers would result in widespread labor shortages.
The notion that this policy might open up jobs for U.S.-born citizens overlooks a critical detail: research suggests that U.S.-born and foreign-born workers often don’t compete for the same jobs. Many immigrants take on roles that are physically demanding or undesirable due to low wages—jobs that domestic workers may not want or be able to fill.
Furthermore, immigrant workers play a key role in job creation by driving demand for goods and services. Reducing the immigrant workforce could lead to closures or scaled-back operations for some businesses due to lost productivity and increased costs of hiring replacement labor.
Price Increases Across the Board
The effect of a reduced immigrant labor force would likely manifest as price increases in several sectors. In agriculture, a diminished production capacity would push food prices up as supply shrinks. Likewise, construction costs would soar due to labor shortages. This scenario would further exacerbate housing affordability issues nationwide, particularly in areas already facing high demand for new homes.
In hospitality and retail, increased operating costs resulting from staffing shortages or heightened wages might be passed on to consumers, causing prices to climb.
GDP Decline
Trump’s proposed mass deportation plan could significantly slash the U.S. GDP. Estimates suggest the economy could face a decline between 4.2% and 6.8%, translating to a substantial loss of $1.1 trillion to $1.7 trillion annually. Such a contraction would be on par with some of the economic downturns witnessed during the Great Recession. This drop is likely attributed to reduced productivity and decreased consumer spending stemming from job losses among both immigrants and U.S.-born workers affected by economic and business slowdowns.
Lost Tax Revenue
Another dimension to consider is the potential loss in tax revenue. Undocumented immigrants contribute significant amounts annually in taxes. In 2022, these contributions totaled $96.7 billion, with $46.8 billion at the federal level and $29.3 billion at state and local levels. Additionally, they contributed $22.6 billion to Social Security and $5.7 billion to Medicare, despite being unable to access these benefits.
Deporting these individuals would sharply reduce these revenue streams, affecting government budgets and services when funding for public services is crucial.
Human and Social Costs
The human cost of such mass deportations is notable as well. Around 5 million U.S.-born children live with undocumented family members at risk of deportation. The possible separation of families poses serious emotional trauma and financial strain on households that depend on these workers as the primary breadwinners.
Communities with large immigrant populations would face social upheaval, as long-standing residents might be forcefully removed from their homes and workplaces. This could swiftly lead to community destabilization and a loss in community cohesion.
Conclusion
Donald Trump’s proposed plan for mass deportations of undocumented immigrants poses numerous challenges, especially for industries that depend heavily on immigrant labor. Although there are arguments suggesting such a policy could open up jobs for U.S.-born citizens or reduce competition for housing by limiting immigrant presence, evidence generally points in the opposite direction. Labor shortages would likely lead to higher food and housing prices and a reduction in overall economic productivity and tax revenue.
In a broader sense, any large-scale deportation could have socially disruptive impacts, affecting not only undocumented immigrants but millions of American families connected to them. The potential for broad economic and social upheaval necessitates a careful re-examination of the proposed policy and its implications across various spheres of society.
To further explore official information on the U.S. immigration policy, please visit the U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) website. Analysis from VisaVerge.com reveals that navigating these complex immigration issues requires thoughtful consideration and a balanced approach, taking into account both economic needs and humanitarian concerns.
Learn Today
Deportation: The act of removing a foreign national from a country due to legal or regulatory violations.
Undocumented Immigrants: Individuals residing in a country without legal permission, often lacking official documentation or authorization.
Labor Shortage: A situation where the demand for workers exceeds the available supply, leading to unfilled job positions.
Economic Disruptions: Significant interruptions in economic activities, impacting productivity, market stability, and financial conditions.
GDP Decline: A reduction in the Gross Domestic Product, indicating a decrease in economic output and national economic health.
This Article in a Nutshell
Donald Trump’s proposed mass deportation policy threatens key U.S. industries reliant on immigrant labor, such as agriculture and construction. Economists warn of labor shortages, increased prices, and economic disruptions. As policymakers debate potential benefits, the risk of social upheaval and financial strain on communities calls for a balanced, humane approach.
— By VisaVerge.com
Read more:
• Germany’s Afghan Migrant Deportations Spark Human Rights Debate
• Trudeau’s Policy on Immigrants: Pathway to Status and Faster Deportations
• Canada Asylum Rules: Proposed Changes to Expedite Deportations
• Australian Immigration Bill: Facing Potential Mass Deportations
• Biden Tightens Asylum Rules, Speeds Up Migrant Deportations at US-Mexico Border









it is an outrageous form of treatment. i get the deportations of so called illegal immigrants{ criminals, those committing federal crimes or even murderers for that matter. it is totally different when children are involved whether they are rightfully given citizenship thru birth or thru naturalization etc. it will eventually create chaos both from a political standpoint and humanity. Now the work force will be drastically shortens and the public opinions will echo thru ages to come even if nothing comes to light. ” racially removed regardless of background” god help us all